| Back to Lesson 11 | ECON 4333 Links | ECON 4333 Page |
Natural Monopoly Regulation
![]()
The (inherently political ) process of natural monopoly regulation has as its end result the establishment of rate levels and rate structures. Viscusi, Vernon, and Harrington point out that while public regulation of local telephone service, natural gas, etc. is based on the principle that such regulation is welfare-enhancing, regulation nevertheless has a profound impact on the structure of incentives facing the regulated firm.
![]()
The regulatory process can be described by the following accounting equation:
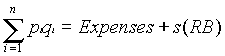
By the term rate level we mean the rates set on the various services provided which, based on estimates of demand at alternate rate levels, will generate revenues sufficient to defray costs of production and generate the allowed rate of return (s).
The term rate structure means the price paid for one service or by one class of customers relative to others or "price discrimination among different classes of buyers and products."
Example
Level 1/Structure 1
User P/KWH
Residential $7.45
Industrial 7.81
Level 1/Structure 2
User P/KWH
Residential $7.50
Industrial 7.50
Level 2/Structure 1
User P/KWH
Residential $8.20
Industrial 8.59
![]()
| Back to Lesson 11 | ECON 4333 Links | ECON 4333 Page |