BOT 1103 - BIOLOGY OF PLANTS – PRACTICE EXAM FOR TEST #3
-
IN PREPARATION FOR REGULAR LECTURE EXAM III SCROLL DOWN TO TAKE THE PRACTICE EXAM AND REVIEW.
-
CLICK HERE TO TO DOWNLOAD AN ANSWER KEY OF THIS PARTICULAR PRACTICE EXAM
PART I: Multiple Choice - Choose the best answer. Be sure to look over all possible choices before making your selection.
1. A recurrent theme in the life cycle of plants is a phenomenon called Alternation of Generations. In terrestrial plants, such as gymnosperms (e.g., conifers) and angiosperms (i.e., flowering plants), which generation is most likely to be the more short-lived generation?
A. The gametophytic generation
B. The sporophytic generation
C. Alternation of generations does not apply to terrestrial or land plants; hence the question is irrelevant.
D. The sporophytic and gametophytic generations are equivalent; neither can be considered short-lived.
E. None of the above choices are correct.
2. The collective term for all the petals of a flower is _________________.
A. androecium
B. gynoecium
C. calyx
D. corolla
E. receptacle
3. Cucumbers produce separate unisexual flowers that are either male or female on the same plant body. These flowers also lack sepals and petals. Each flower on such a plant would be considered ______.
A. perfect and complete
B. perfect and incomplete
C. imperfect and complete
D. imperfect and incomplete
E. sterile
4. When the calyx, corolla, and stamens of a flower are attached to the receptacle in a position above the ovary, the ovary of the pistil or carpel is said to be _______________________.
A. superior
B. inflated
C. mediocre
D. inferior
E. average
5. In flowering plants, the process of _____________ is integrated into the formation of spores (sporogenesis) that develop into the male or female gametophyte, whereas the production of gametes (gametogenesis) is associated the nuclear division known as ___________________.
A. meiosis; mitosis
B. mitosis; meiosis
C. meiosis; meiosis
D. mitosis; mitosis
E. More than one of the above choices are correct.
6. Homologous chromosomes _______________________.
A. are similar in size and length
B. have the same centromere position
C. carry the same kinds of traits or genes
D. have different parental origins
E. All of the above are correct.
7. In which phase of meiosis does crossing‑over occur and chiasmata are seen?
A. prophase I
B. prophase II
C. metaphase I
D. metaphase II
E. anaphase II
8. Based on independent assortment of chromosomes during Metaphase I of meiosis, what is the the probability of two gametes being produced simple cell division (mitosis) by two gametophyte parents that originated from the sporophyte of a pea plant (2N = 14 or 7 pairs of chromosomes) that form the same assortment of chromosomes and these combining after fertilization to form an offspring identical to one of its siblings is at least __________.
A. 22 or 1 in 4
B. 27 or 1 in 128
C. 1282 or 1 in 16,384
D. 72 or 1 in 49
E. 497 or 1 in 67,822,000,000
9. In sexually-reproducing organisms, novel or new genetic combinations are produced through ____________.
A. crossing-over and genetic recombination during meiosis
B. independent assortment of homologous chromosomes during meiosis
C. the process of fertilization (the fusion of two gametes)
D. sporogenesis
E. All the above are correct
10. Through the process of "double fertilization", most flowering plants (approximately 70% of all species - Polygonum type) produce a ________________ zygote and a triploid (3n) endosperm.
A. haploid (1n)
B. diploid (2n)
C. triploid (3n)
D. pentaploid (5n)
E. hexaploid (6n)
11. Botanically speaking a fruit, such as a cherry, pecan, or a coconut, with a fleshy exocarp and mesocarp, and a stony hard endocarp surrounding a single seed is a ________________.
A. Berry
B. Pepo
C. Hesperidium
D. Pome
E. Drupe
12. Which of the following would be classified botanically as “true berries”?
A. apple, pear
B. tomato, grape
C. corn, wheat
D. orange, lime
E. cherry, peach
13. When the pericarp of the fruit is dry and splits open at maturity to release the seeds inside (e.g., legume, follicle, capsule), the fruit is said to be ______________.
A. dehiscent
B. indehiscent
C. fleshy
D. robust
E. Choices B and C are both correct.
PART II: LABEL THE DRAWING.
1. DRAW A DIAGRAM AND LABEL THE PARTS THAT ARE FOUND IN A COMPLETE FLOWER WITH AN INFERIOR OVARY (OR WHICH EXHIBITS EPIGYNY).
2. DRAW A DIAGRAM AND LABEL THE PARTS THAT ARE FOUND IN A FLESHY FRUIT LIKE A DRUPE OR A BERRY. DISTINGUISH BETWEEN THE DIFFERENT REGIONS OF THE PERICARP.
3. DRAW A DIAGRAM AND LABEL THE PARTS THAT ARE FOUND IN A POLLEN GRAIN (MALE GAMETOPHYTE) AND AN EMBRYO SAC (FEMALE GAMETOPHYTE) OF “TYPICAL” FLOWERING PLANT.
PART III: FILL IN THE BLANKS.
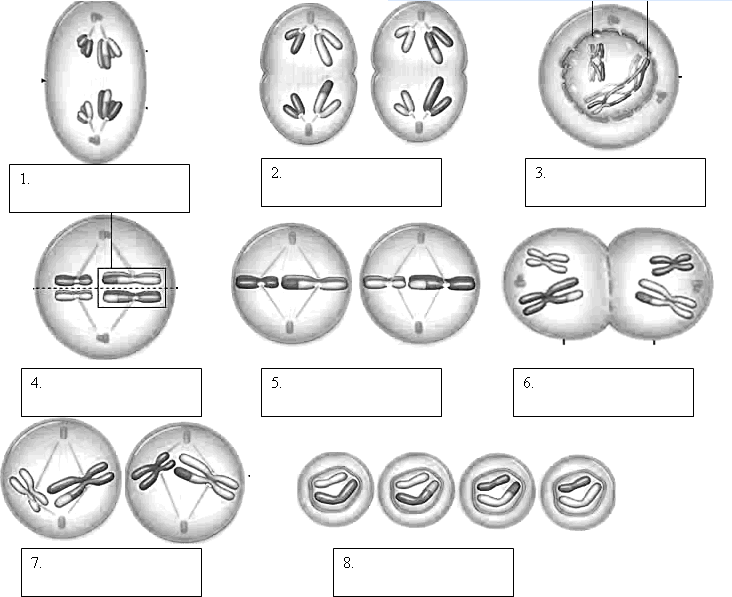
1. FILL IN THE BLANKS FOR THE VARIOUS STAGES REPRESENTED IN THE FOLLOWING TEXT OR DIAGRAMS FOR MEIOSIS.
Phases of Meiosis
Name of Phase Description 1. Homologous chromosomes pair up and form tetrad OR BIVALENTS 2. Spindle fibers move homologous chromosomes to opposite sides 3. Nuclear membrane reforms, cytoplasm divides, 4 daughter cells formed 4. Duplicated chromosomes line up along equator, not in homologous pairs 5. Crossing-over occurs 6. Chromatids separate 7. Homologs line up alone equator 8. Cytoplasm divides, 2 daughter cells are formed